Mobile Phones Overview
A mobile phone (also known as a cellular phone, cell phone, hand phone, or simply a phone) is a device capable of making and receiving telephone calls over a radio link while moving around a wide geographic area. It achieves this functionality by connecting to a cellular network provided by a mobile phone operator, granting access to the public telephone network. In contrast, a cordless telephone operates within the short range of a single, private base station.
Common Components
- Battery: Provides the power source for the phone functions.
- Input Mechanism: Allows users to interact with the phone. Commonly, this is a keypad, but touch screens are prevalent in most smartphones.
- Screen: Displays the user's typing, text messages, contacts, and more.
- Basic Mobile Phone Services: Enable users to make calls and send text messages.
- SIM Card: Found in all GSM phones, it allows an account to be swapped among devices. Some CDMA devices also utilize a similar card called a R-UIM.
History of Mobile Phones
The history of mobile phones focuses on communication devices that wirelessly connect to the public switched telephone network. The transmission of speech by radio has a long history, tracing back to Reginald Fessenden's invention and shore-to-ship demonstration of radio telephony. Early mobile telephones were significantly less portable compared to today's compact hand-held devices. Over time, advancements in technology have led to more portable devices and significant changes in wireless communication networking.
The world's first mobile phone call was made on April 3, 1973, by Martin Cooper, a senior engineer at Motorola. He called a rival telecommunications company, marking a milestone in mobile communication history.
SIM Card
GSM feature phones require a small microchip known as a Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) card to function. These cards are approximately the size of a small postage stamp and are typically placed underneath the battery in the rear of the unit.
Introduction to Mobile Operating Systems
Operating System: An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources and provides common services for computer programs. It acts as an intermediary between programs and computer hardware, facilitating functions such as input/output operations and memory allocation.
Mobile Operating System: Mobile operating systems are specifically designed for mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. They facilitate user interaction through touch gestures and provide various services tailored to mobile usage.
Java OS (J2ME):
- Description: J2ME (Java 2 Platform, Micro Edition) is a set of technologies, specifications, and libraries developed by Sun Microsystems for small devices like mobile phones and pagers.
- Platforms: It includes high-end and low-end platforms catering to different classes of devices.
- Licensing: J2ME is licensed under GNU General Public License.

Android:
- Description: Android is a mobile OS developed by Google, based on the Linux kernel. It is primarily designed for touchscreen devices.
- User Interface: Android's user interface relies on touch gestures for direct manipulation of on-screen objects.
- Variants: Apart from smartphones and tablets, Android is used in devices like Android TV, Android Auto, and Android Wear.
- History: Initially developed by Android, Inc., Google acquired it in 2005. It was unveiled in 2007 with the founding of the Open Handset Alliance.

iOS:
- Description: iOS, originally known as iPhone OS, is a mobile OS developed by Apple Inc. exclusively for Apple hardware, including the iPhone, iPad, and iPod touch.
- Foundation: iOS is based on Mach Kernel and Drawing core, which are also present in Mac OS X.
- Preemptive Multitasking: iOS supports preemptive multitasking, allowing seamless switching between tasks.
- Address Space: Each application in iOS has access to its own 4 GB address space.

Overview of Mobile Operating Systems
Ubuntu Touch (Ubuntu Phone):
- Description: Ubuntu Touch, developed by Canonical UK Ltd and the Ubuntu Community, is a mobile version of the Ubuntu operating system. It targets touchscreen mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets.
- Release: Announced by Mark Shuttleworth in 2011, Ubuntu Touch was released to manufacturers in September 2014. The first Ubuntu-based smartphone, Bq Aquaris E4.5, was launched in Europe in February 2015.

Tizen:
- Description: Tizen is an open-source operating system based on the Linux kernel and API. It caters to a wide range of devices including smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, and more.
- Purpose: Tizen aims to offer a consistent user experience across various devices. It is governed by the Tizen Association and supported by companies like Samsung and Intel.

Windows Phone (WP):
- Description: Windows Phone, developed by Microsoft, is a family of mobile operating systems intended as a successor to Windows Mobile and Zune. It features a user interface derived from the Metro design language.
- Evolution: Launched in 2010, the latest public release is Windows Phone 8.1, with Windows 10 Mobile succeeding it. Windows 10 Mobile emphasizes integration with PC counterparts and an expanded application ecosystem.
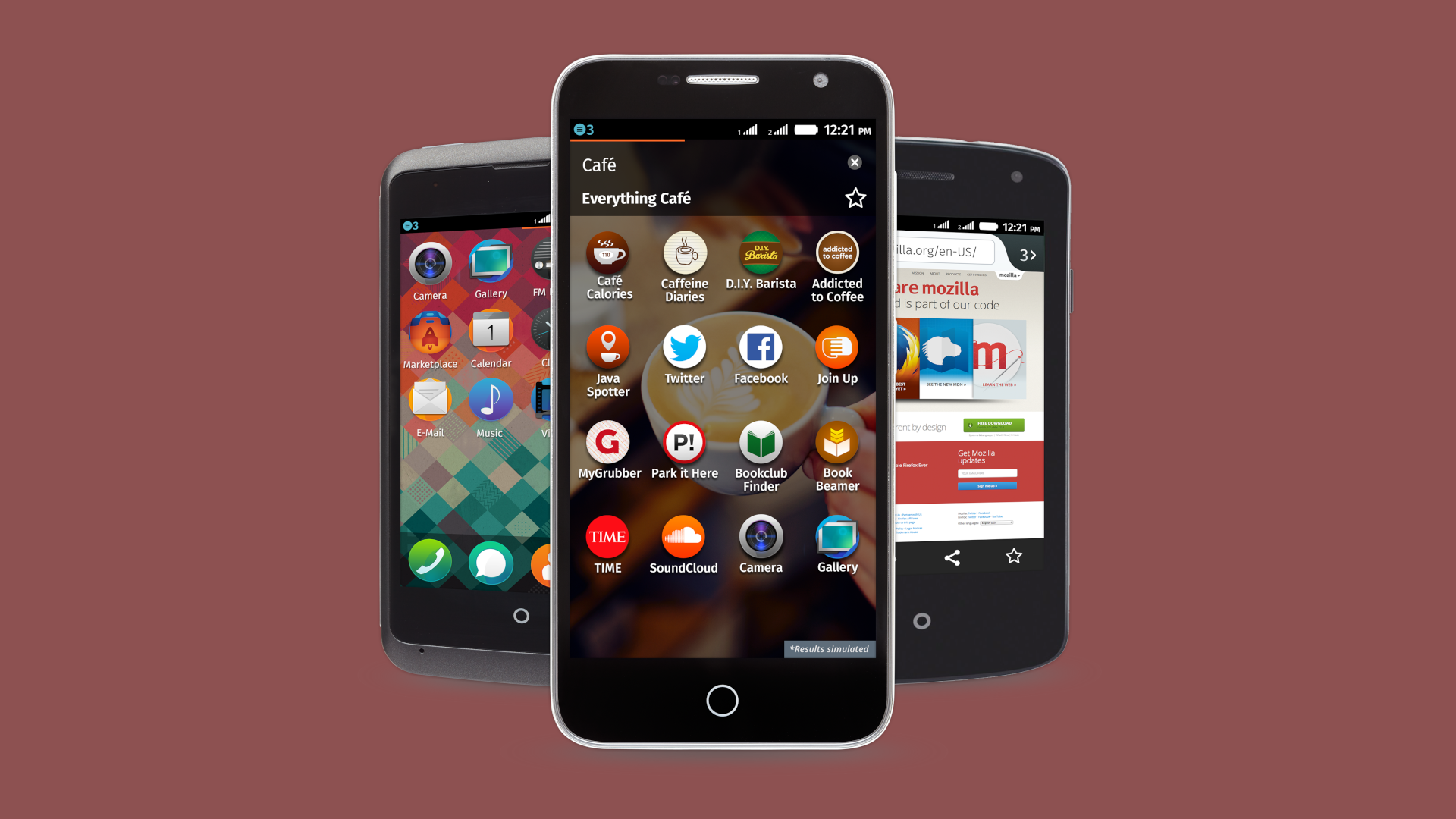
Firefox OS:
- Description: Firefox OS is an open-source operating system developed by Mozilla, primarily targeting smartphones, tablet computers, and smart TVs. It utilizes HTML5 applications, JavaScript, and open web APIs.
- Release: Publicly demonstrated in 2012, the first commercial Firefox OS phone, ZTE Open, was launched in Spain in 2013. Firefox OS devices are offered by multiple operators in various countries.

Symbian:
- Description: Symbian is a mobile operating system designed for smartphones. Initially closed-source, it became open-source under the Symbian Foundation in 2009. It was popular until overtaken by Android in 2010.
- Principles: Symbian OS was developed with principles emphasizing data integrity, efficient use of user time, and resource scarcity management.

BlackBerry OS:
- Description: BlackBerry OS, developed by BlackBerry Ltd., is a proprietary mobile operating system for BlackBerry handheld devices. It supports multitasking and specialized input devices like trackballs and trackpads.
- Features: Known for its native support for corporate email and synchronization with Microsoft Exchange, Lotus Domino, or Novell GroupWise, BlackBerry OS has been popular in enterprise environments.
